Introduction
Brand Management strategies of Unilever will be evaluated in this report. Brand refers to the incorporeal image and approaches to a product or services of a company (Ertimur, and Coskuner-Balli, 2015). In this report, the way of building and managing a brand over time has been demonstrated. The ways by which brands organize their portfolios have been evaluated. The process of leveraging brands over time domestically and internationally has been also demonstrated. In the last part of the report, the techniques for measuring and managing brand value over time have also been evaluated. Unilever has been selected to show the techniques and methods of managing brands and strategies for making a successful brand. Unilever is a British multinational consumer products industry that provides services across the world. And it is one of the most dominating consumer brands in the world.
You may feel interested to read below blogs:
Marketing strategies of IKEA in the Chinese Market
How to deliver excellent customer service
Marketing strategies of Uber
Importance of branding as a marketing tool
Branding is a significant marketing tool which helps customers to identify a product and distinguish it from available products and services in the market (Keller, Parameswaran, and Jacob, 2011). It creates an outstanding impression on customers’ minds. The importance of branding and the reasons for its emergence in business practices are evaluated below:
Branding boosts up recognition: Key component of a brand is its logo, and customers recognize the brand when they see the logo of a brand (Heding, Knudtzen, and Bjerre, 2015). The design of the logo of a brand creates an anticipated impression on customers’ minds about the company. Unilever tries to design its logo with a positive and modern design in order to represent its business in a better way. With a modern design and attractive logo, the company shows the different programming and services that they offer. Though a logo is the face of a company, the logo should be designed easily so that customers can easily remember it. For example, the logo of Unilever is simple that customers can remember easily and it is enough to power to make an outstanding impression on customers’ minds.
Increases business value: When companies have a target to take their business ahead in future, branding helps them a lot to enhance their business (Kapferer, 2012). By establishing a strong brand, Unilever increases its value and gets more power in the industry. After having more power in the industry through branding, the company gets more investment opportunities because the company is known as one of the most established businesses in the market. It becomes easier for companies to borrow funds or progress out to an IPO. As a result, the company can expand their business easily and get a better financial return from the effort they deliver.
Increases sales: Though customers have trust in strong brands, they purchase more from the brand (Rosenbaum-Elliott, Percy, and Pervan, 2015). They maintain repeated sales and even suggest others make purchases from the brand. Therefore, Unilever becomes able to generate higher revenue by boosting sales. Branding also makes companies’ competitive advantage stronger by making a unique image in customers’ minds and in the marketplace. As a result, sales remain higher and revenue also tends to increase more.
Protects from competitors: Branding safeguards the copyright of a company and emerges business practices through protecting companies from their competitors (Barrow, and Mosley, 2011). Competitors cannot copy the signature product or service of an established brand which made them leaders of the market. As a result, Unilever can avoid the risk of being copied by competitors. Competitors can make similar products but have no permission of making a signature product which maintains the leading position of companies.
Wins customers’ trust: By building a brand, companies win customers’ trust (Kapferer, 2012). Brand refers to good quality products and services with good reviews and ratings. Therefore, Unilever can attain customers’ trust more through branding. Even customers’ have a positive image of a brand that they are treated fairly, and their services are addressed quickly. Customers know that they will get better products and services from a brand. Therefore, they trust established brands in the market when choosing products or services.
Generates new customers: Strong brand refers to the positive impression of a company on customers’ minds (Barrow, and Mosley, 2011). New customers consider the brand when they make a purchase decision. Branding is one of the most effective marketing techniques that Unilever can use to attract new customers in huge numbers. As a result, the sales of a company increase and they can generate higher revenue.
Supports advertising: Though a brand creates positive thoughts about a company and their products and services, it supports advertising of the company (Hanna, and Rowley, 2011). Customers feel confident about the products and services of established brands therefore customers maintain repeatable sales from the company. Logo, packaging and printed materials are the parts of a brand that helps a company to differentiate its products and services from the competition. It seems that branding works better as one of the most efficient advertising methods.
Increases employees’ satisfaction and pride: It is a great honour for employees when they work for an established brand (Barrow, and Mosley, 2011). Employees feel happy being a part of the brand, and it creates job satisfaction. They find themselves reputed while working for the brand because everyone knows the brand. Therefore, employees who enjoy their work and deliver better performance with high satisfaction for Unilever. Because of employees’ satisfaction and their better effort, Unilever is able to bring more outstanding output that emerges from business practices.
Effective brand strategy for building and managing brand equity:
Brand strategy refers to the plan that includes exact, durable goals which can be attained with the progress of a successful brand and the joint components of an organization’s attractiveness which makes it unique (Ashworth, and Kavaratzis, 2010). A well-defined and effective brand strategy influences all traits of a business and has a direct connection with customers’ emotions, needs and competitive environments. Components for a successful brand strategy for building and managing brand equity are evaluated below:
Defining business purpose: Companies have to have the defining purpose for their business in order to separate their brand from another (Jin, 2012). Specific business purpose makes a brand different from its competitors. The business purpose of an organization can be focused on immediate success in order to make money. Even companies can target success to make money by doing good for the world. Unilever’s purpose is to focus on success to make money by doing good for the world. For example, Unilever’s purpose is to produce the best products at a lower prices therefore people of every status can afford the products. This defined business purpose refers to the intention of the company that they want to make the world better and generate profit.
Consistency: Companies have to escape speaking about the things that do not develop a brand and it is one of the keys to consistency (Atwal, and Williams, 2017). They should not deliver any message that confuses the audiences because brand recognition is influenced positively by consistency and it boosts customers’ loyalty. Companies have to make sure that the messages they deliver to the customers are organized therefore customers will be able to get a clear idea about the company. For example, Unilever’s promise toward consistency let every essential of the brand’s marketing give effort together which helped the company to be one of the most famous brands across the world.
Emotional branding: Emotional branding attracts customers toward the brand instead of purchasing similar products and services from another brand at lower prices (Jin, 2012). Through emotional branding, companies make people feel that they are a part of the brand. People have a basic psychological need to feel attached to others and companies utilize this human nature as an effective way of making a successful brand. Emotional branding strengthens the relationship with customers and fosters customer loyalty. For example, Unilever uses the slogan ‘Dirt is good for Surf Excel detergent and it helps them to create an emotional attachment with the people of India. Make emotional advertisement for Indian people and successfully make them emotionally attached to Surf Excel therefore people purchases this detergent the most.
Creative campaign: In this competitive business world, companies should be enough flexible to stay relevant and conduct a creative campaign to ensure continuous sales (Atwal, and Williams, 2017). Flexibility enables companies to make adjustments that construct interest and differentiate the approach of the brand from the competition. For example, between new commercials, a new website, new packaging, and new products, Dove soup of Unilever has managed to hold onto its customer base by utilizing its strategic enhancements. Dove did not lose its demand and increased demand by using a creative campaign.
Reward customers: Companies have many customers who love them therefore companies can reward the customers for their love (Jin, 2012). There are many customers who purchase from the brand they love and suggest others make purchases furthermore act like brand ambassadors. By rewarding these customers, a brand will show its loyalty to them, which will bring more returning customers. As a result, the company’s brand becomes stronger and generates more revenue. For example, Unilever rewards their customers who watch their advertisement on the Dove Men+ Care range through a mobile app (Digital Strategy Consulting, 2012). Customers get reward points for buying discounted products or free products of a specific range.
Social media campaign: Social media is one of the most effective ways of promoting a brand. Companies can ensure a strong presence in social media to stay connected with customers through Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Pinterest etcetera. It will help them to inform customers about the products and services easily because most people use social media in the present day. It will help companies to manage brand equity at a lower cost and will get the most effective result.
Different strategies of portfolio management, brand hierarchy and brand equity management
Brand portfolio strategy of Unilever
A full set of brands and brand lines offered by an organization to the market is called a brand portfolio (Atwal, and Williams, 2017). When each brand is considered a complement to other brands, it is stated as an ideal brand portfolio and every company desire to face this situation in its brand portfolio. Companies should have a well-defined set of brand portfolio strategies in order to attain long-term prosperity. Unilever is one of the top companies that hundreds of brands in their brand portfolio and all the brands are not offered in all areas of the world. The portfolio brand management strategies of Unilever are evaluated below:
Differentiate brands: Unilever applies a differentiation strategy in similar products therefore, every brand is different from one another (Dirisu, Iyiola, and Ibidunni, 2013). Every product of the same category brings different features. For example, Colgate and Close Up are both famous toothpaste of Unilever, but they have different qualities. Colgate makes teeth strong with its calcium seal formula and makes teeth whiter. Whilst Close-up gives freshness with its mouth fresh formula. As a result, customers who want strong teeth purchase, and those who want freshness purchase Close Up.
Reduces the overlap: Companies work to make a brand portfolio where brands do not compete with each other and stopping brands’ competition in a brand portfolio is called reducing overlap. Unilever ensures that their brands of similar products will not compete with one another (Calder et al, 2010). For example, Sun silk and TRESsemme are both the shampoo brands of Unilever. Customers know the difference in the result of these shampoos. Therefore, they do not compare Sun Silk with TRESsemme, and both shampoo brands have different customers base.
Application of branded property model: Unilever applies branded property model (Devine, and Williams, 2016). The company makes different brands with different names. Every brand is known by its own name. For example, Unilever has hundreds of brands, but the company do not add the name ‘Unilever’ with any brand and keeps the different name of a different brand. Therefore, the negative impact of a brand has no influence on other brands of Unilever.
Covers major markets: Unilever ensures the global presence of all brands of them in the major markets that increase their demand globally (Laursen, and Andersen, 2016). The company have dominance in the beautification industry, hair and care industry, beverage industry, food industry, etcetera. Because of its dominance in most of the sectors in a major market, Unilever has become successful in creating so many customers globally. Customers from all countries get the different brands of Unilever near their hands, and it boosts the demand for their brands.
Brand portfolio of Unilever:
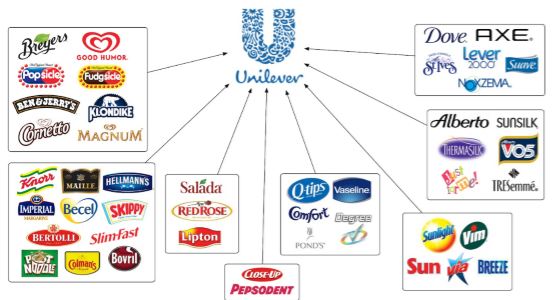
Adapted from: Pinterest, 2020
Brand hierarchy management of Unilever:
Unilever has products in four categories such as home care, beauty products, water purification and food & drink. There are many brands under these categories. The brand hierarchy of Unilever is stated below:
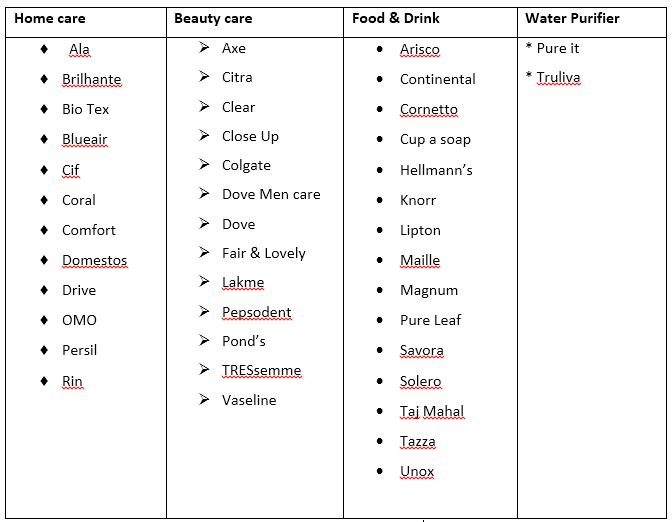
Strategies of managing brand equity of portfolio of Unilever:
Brand equity refers to the marketing term that shows the value of a brand (Phan, Thomas, and Heine, 2011). Brand equity is stated on the basis of customer perception and experiences with that brand. The strategies Unilever uses to manage its brand equity of portfolio are evaluated below:
Understands competition and applies differentiation: Unilever does industry analysis to understand the competition they may face and the attitudes of customers when they provide services in the global market (Pant, and Ramachandran, 2017). It helps them to manage brand equity. For example, it has identified the competition in soup market and produced Lux for customers who want perfume with beauty benefits furthermore produced Dove for customers who want moisture with beauty soap.
Focuses on cultural concerns: Unilever considers cultural concerns while branding the products of the portfolio in a different areas of the world (Kaur, 2013). Even the company set the names of many products after considering cultural concerns. For example, Surf Excel is one of the famous brands known by this name in Asian countries. Whilst it is named ‘Ala’ in many countries according to the cultural concerns of the area.
Knows the details about targeted customers: Unilever finds out the demand of targeted customers and their financial condition before providing services to a market (Sim, King, and Price, 2016). For example, Unilever realizes the condition of Indian lower-class people and bring their products, such as toothpaste, shampoo, cream, detergent etcetera in mini packs. As a result, people can purchase their products which are financially weak.
The process of brand’s leverage over time:
Unilever’s strategies for managing collaboration and partnership at domestic and global levels:
The strategies of a brand through which companies build the value of their existing brand strength are brand leverage (Rauschnabel et al., 2016). Brand leverage is significant for Unilever.
Strengths of Unilever:
Unilever is one of the leading consumer goods businesses in the world. The strengths of the company are evaluated below:
Great global presence: Unilever has its presence in 190 countries of the world (Unilever: 2, 2020). It refers to the great coverage of the country. People of all countries get Unilever’s products in their hands, and it makes the company highly profitable. Unilever can leverage this strength in order to increase its market share to capture more customers globally from the area where they have no service.
Broad portfolio of brands: Unilever has a broad portfolio, and all the brands are successful in creating an outstanding image in customers’ minds (Poonamallee, 2011). This broad portfolio makes its position stronger in the global market. It will also help Unilever to leverage more market share.
Heavily funded R&D initiatives: Unilever invests huge amounts in the R&D sector, helping them to produce a similar type of products with different features (Nurfadillah, 2016). Unilever can produce more innovative products that will help people to make their life better. Unilever can utilize this strength to leverage market share by producing more new products in the area that they have not entered yet.
Flexible pricing: Unilever uses a flexible pricing approach, therefore, people of all types of financial ability can purchase their products (De Campos, 2010). It has products of all ranges for all types of customers. For example, TRESsemme shampoo is more costly than Sun Silk, and customers of higher budget purchase TRESsemme furthermore, lower budget customers purchase Sun Silk. Unilever can leverage this opportunity to maintain its customer base and remain highly profitable.
Weakness of Unilever:
Unilever has some weakness also that makes its growth slower than expected. The company should remove the weakness to boost its success. The weakness is:
Presence of other global competitors: The global presence rate of the competitors of Unilever, such as P&G, Nestle and other local companies, are close to Unilever’s presence (Jurietti, Mandelli, and Fudurić, 2017). They can replace Unilever’s position very soon by capturing the customers of Unilever.
Recommendation: Unilever should make its position stronger by taking necessary steps, such as: enhancing the quality of existing products. Therefore, customers will not switch to Unilever after getting better products than before.
Products can be replaced: Unilever greatly depends on retailers because the company sells its products through retailers (Ansah, and Poku, 2013). Therefore, Unilever is unable to influence its customers directly. Retailers influence the customers directly and refer to the less marketing efforts of the company.
Recommendation: Unilever should enhance its marketing effort in order to make direct connections with customers. It will help the company to know about customers’ demands and they will be able to enhance the quality according to customers’ demands. Unilever can open its own outlet in the major markets to make direct connections with customers.
Collaboration and partnerships of Unilever:
Unilever can make partnerships and collaborative agreements with different types of organizations across the world to make its execution more effective. This partnership and collaboration will help the company to cope with different types of problems. It will also help Unilever to increase customers satisfaction.
Agreement with suppliers: Unilever has to make an agreement with suppliers who deliver better raw materials. For example, without the best mechanisms, Unilever will not be able to make their water purifier the most effective on finishing germs.
Agreement with national health authority: By making an agreement with the national health authority, Unilever will be able to get better knowledge in developing the quality of their health-related products.
Collaboration with world-famous dermatologists: By collaborating with world-famous dermatologists, Unilever will be capable of improving its skin care products more than before. Therefore, the demand for their skin care products will increase.
Agreement with ISO: Unilever can get certification from ISO on its quality level. And it will increase the acceptance of Unilever’s products enormously because customers will be more relaxed about the quality of the products. Therefore, sales of Unilever will be fostered.
Techniques for measuring and managing brand value:
Brand value is an intangible asset of companies. It refers to the comparison of an organization’s book value and market value (Iglesias, and Bonet, 2012). Brand value is also known as brand equity. There are many ways to measure the brand value of an organization. These ways are stated below:
By measuring the total number of customers, the buyer product industry can measure its brand value.
A payment that customers remain ready to pay also refers to the brand value of a company. For example, if customers are ready to pay a higher price, it refers higher brand value of the company.
A repeated number of customers refers to the good brand value of a product.
Repeated purchases of customers indicate customers’ loyalty toward the brand and high brand value.
Brand value depends on some specific features of a brand, such as quality products that boost the brand value of an organization. A company builds up its brand value by delivering better products and services over a long time. For example, TRESsemme is a more costly shampoo than Pantene, but customers are ready to pay the high price for its brand value.
Brand awareness shows brand value:
Customers’ awareness of a brand and the products and services of the brand is called brand awareness (Temporal, 2011). Companies have to create brand awareness to promote their products and services. By creating brand awareness, companies make themselves different from their competitors. Creating brand awareness boosts the sales of a company, and companies should create brand awareness when they launch new products. For example, if anyone thinks about beauty, soap will think about Lux and Dove at first. Unilever has developed these brands on their own name and used strong strategies to build brand awareness. Increasing brand awareness helps to build brand equity. Advertisements on TV, mouth publicity, social media, sponsorships, etcetera are ways of creating brand awareness. For example, Unilever has increased brand awareness about Lux by advertising on TV channels with superstars of Bollywood and Hollywood.
Market Share implies brand value:
Market share refers to the number of sales that a company makes in a market (Zenker, and Braun, 2010). It refers to the level of dominance that a company has in a specific market compared to its competitors. The amount of market share refers to the power of a company. Companies with higher market share are considered the most powerful company in the market. It takes a long time to attain market share, and it is a long-term process. Companies have to deliver quality products are services, maintain a good relationship with suppliers and become more customers focused on attaining the highest market share.
The rate of customers’ partialities for a product or service also indicates market share. High sales rate, high brand value, and high demand for products and services are indicates a high market share of an organization. For example, Unilever’s shampoo possesses a 17.1% share of the shampoo market, whilst P&G possess 13.9% (The wall street journal, 2019). The shampoo market share refers to the high market share of Unilever shampoo brands, and it also shows customers’ loyalty toward the shampoo brands of Unilever. The higher market share and customer loyalty assist companies in enlarging their business in new or existing markets, which makes the companies competitively stronger.
Brand value is reflected through Customers’ Attitudes:
One of the most valuable assets for a company is customers’ perception of a brand. Customers’ belief about products and services, feelings about the products and services furthermore behavioural purpose about the products and services refers to customers’ attitude (Qian, Y., 2014). Customers’ beliefs are made from their regular observations, such as girls believing that Dove is the most effective soap which is suitable for all skin types and makes skin healthier. In customers’ attitudes, feelings play an outstanding role. For example, customers think that Surf Excel protects white clothes and cleaners.
Purchasing intent of customers also expresses brand value:
Customers go through several segments when before they purchase anything, and purchasing intent is one of that segments (Hanna, and Rowley, 2013). Purchasing intent refers that customers’ intention or interest to buy a product or service. For example, customers evaluate the effectiveness and compare Colgate, Pepsodent and Colgate before purchasing toothpaste then they choose one among the toothpaste. It shows that customers think about different factors when they purchase any product or service. Even they will consider the brand which is well known in the market and create value for money.
Conclusion
Customers are concerned about brands in case of purchasing products and services. Therefore, companies should focus on branding to attract more customers toward them. Customers always choose the well-established brand of a company from the available brands. Companies have to focus on enhancing the quality of their services and products because quality boosts brand value. By increasing brand value, companies will be capable of competing in the market strongly. As a result, sales of the brand will remain higher than the competitors.
References
Atwal, G. and Williams, A., 2017. Luxury brand marketing–the experience is everything!. In Advances in luxury brand management. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham.
Digital Strategy Consulting, 2012. Unilever rewards customers for watching ads via mobile app. Retrieved from: http://www.digitalstrategyconsulting.com/unilever-research-tips-and-news-for-marketers/unilever-rewards-customers-for-watching-ads-via-mobile-app/8011/. [Assessed on: 15 March 2020]
Pinterest, 2020. Unilever. Retrieved from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/369858188117399584/. [Assessed on: 16 March 2020]
The wall street journal, 2019. Shampoo Giants Go Head to Head. Retrieved from: https://www.wsj.com/articles/unilever-cuts-prices-as-shampoo-rivalry-grows-11571302051. [Assessed on: 19 March 2020]
Unilever: 2, 2020. Who we are. Retrieved from: https://www.unilever.com/about/who-we-are/. [Assessed on: 18 March 2020]
Zenker, S. and Braun, E., 2010, June. The place brand centre–A conceptual approach for the brand management of places. In 39th European Marketing Academy Conference, Copenhagen, Denmark.
