Introduction
Consumer Behaviour and Insights in Hospitality Industry will be evaluated in this report by applying the required theories and models. A comprehensive understanding of Consumer Behaviour (CB) within the hospitality industry plays a crucial role in the process of business growth. The aim of this study is to produce an insight into consumer behaviour from the perspective of marketing analyses working in the hospitality industry. Premier Inn, a UK-based hospitality industry, is the largest hospitality service provider serving a wide range of consumers by providing a range of facilities with 72,000 rooms and 800 hotels in the UK, Ireland, Germany, UAE, and Qatar (Premier Inn., 2020). The hotel company is owned by Whitbread Plc. Overall, the implication and influence on the business growth of this selected entity have been observed and illustrated here in light of the concept of consumer behaviour.
You may feel interested to read below blogs:
Tourism strategies for Broadstairs coastal area
Importance of Managing Service Quality in the Tourism Sector
Resort Management Strategies of One&Only
Sustainable Tourism Planning for Costa Rica
Customer Service Management of Premier Inn
Impacts of cultural, social, personal and psychological factors on consumer behaviour and attitudes
Consumer behaviour represents buying behaviour of consumers, and analysis of this is a beneficial approach to understanding the buying intention of a consumer or a group.
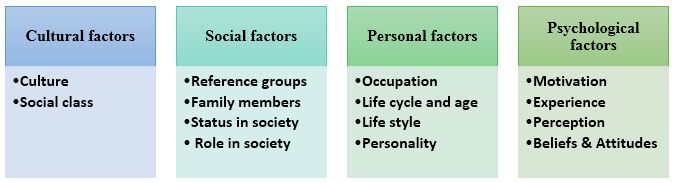
Cultural Factors: Culture is defined as a distinctive way of life in society (Kotler & Armstrong, 2010). People grow up with certain norms, values, attitudes, and beliefs of a particular environment, those sets of norms, values and beliefs are their culture. Consumer behaviour and attitudes will widely vary based on cultural differences. Wang &Yu (2017) reported that consumer behaviour and attitudes in the hospitality industry are even more complicated in terms of cultural variations. The reason is that the hospitality industry is service-oriented and people of different cultures have different values and perceptions towards services. For example, an Asian family even living in the UK would believe in a joint family because Asians demonstrate higher scores in collectivism as per Hofstede’s Cultural Dimension Model (Kotler & Armstrong, 2010). Such families would be looking for group (family) packages and benefits in hospitality company such as Premier Inn. In contrast, a British or American family are more likely to demonstrate individualism and would prefer small (consisting of parents with one child) offers and packages.
Social Factors: Social factors include reference groups (friends, followers, co-workers etc.), family members, status in society, and role in society (Panwar et al., 2019). The Decision-making process of consumers in the hospitality industry is highly influenced by social factors and the social role and status to which the person belongs. While making the decision to consume hospitality services, people widely use word of mouth (WoM), and they ask co-workers or fiends about the services of a certain companies. In such case, ranking in social media (such as Trust Pilot or Facebook reviews) by reference groups highly motivate people to make hospitality consumption decision.
Personal Factors: This includes Occupation, Life cycle and age, Lifestyle, and Personality of the consumer (Dixit, 2017). Personal factors are the most potential and influential factors to motivate consumers to behave in certain ways in making consumption decisions in the hospitality industry. For example, occupation determines the income level and types of jobs a consumer performs. For example, a business executive requiring frequent foreign travel will look for business class suits located in urban areas for convenient business meetings.
Psychological Factors: Motivation, perception, experience and learning gathered from previous incidents, beliefs, and attitudes are the most prominent sub-factors of psychological influence affecting consumer behaviour (Nash, 2019). For example, a previous customer of Premier Inn, being highly satisfied with the excellent services of the hotel group, will demonstrate a high probability of selecting Premier Inn again in upcoming stays. The reason is that the hotel group impressed the customers with a positive attitude and sustainable influence on consumer psychology.
How consumer trends are changing for the influence of digital technology
Technological advancements not only several institutionalized shifts in the operational process of the hospitality industry but also impacted consumer behaviour and its trends. Kanagal (2016) revealed that technological advancements and their incorporation into the tourism and hospitality industry have a significant impact on consumer behaviour. The evolution of digital technologies has changed consumers’ habits of how they book services, how they control room devices, and how they manage surrounding foods and services. The digitization process in the hospitality industry is making the entire process a smoother one, and an easy booking process is an example of such transformation. As demonstrated by Sudha & Sheena (2017), it is time to bring digital transformations to the organizational periphery to cope with changes occurring around the globe. In this perspective, if Premier Inn is not able to cope with the same, consumers are facing dissatisfaction and causing a significant lowering in business level.
The evolution of digital technologies has motivated consumers to check rates online and to make bookings online along with taxicabs booking from the airports (Bowie et al., 2016). Premier Inn has responded accordingly. The Telegraph (2014) reported that Premier Inn invested £35 million in high-tech making the hotel one of the most technologically advanced hotel groups. The hotel group introduced a mobile-based app called Hub which can manage to book, and control room devices (temperature, lighting etc.), working as an alternative to a local guide through navigating surroundings and local foods and cultural sites and heritages. For instance, a consumer can use the app to book a nearby restaurant for dinner, or the consumer can change room temperature through the app. All these changes and the evolution of technology have happened due to the worldwide development of digitalization. All these initiatives taken by the hotel group have significantly affected consumer perception and decision-making.
The present era of transformation with a digital driver is making the process of customer desire-centric methodology. Within this perspective, organizational changes are also to be done so that it can contribute rationally towards changed perception evaluation of consumers. By identifying social networking systems as the most prone and cumulative approach towards the digitization process, Ruiz-Mafe, Chatzipanagiotou, & Curras-Perez (2018) have stated that sharing of information from one consumer to another through social media has become important affecting consumer behaviour. This, in turn, is creating a more comprehensive perspective towards the attainment of a higher degree of customer appreciation. As the information-sharing process is becoming easier in the context of customers, the management authority of Premier Inn is focusing on the maintenance of tremendous social support by analysing changes in trends in regard to social, cultural, personal and psychological aspects.
Stages of consumer decision-making journey:
The figure demonstrates the stages involved in the consumer’s decision-making journey.
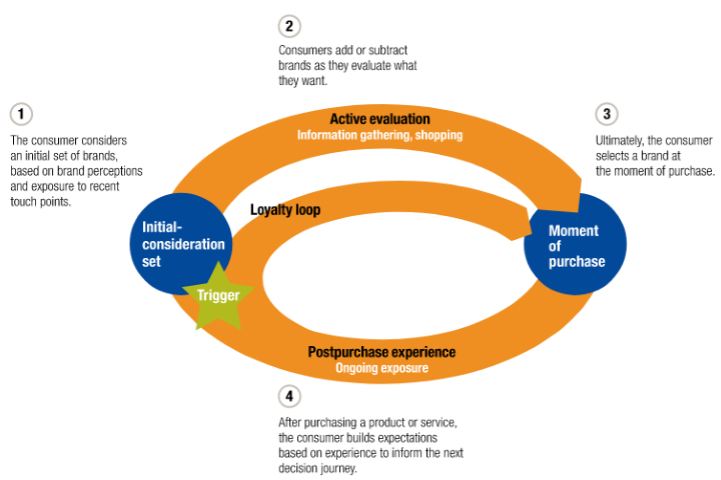
Consumer’s decision-making journey (McKinsey & Company, 2019)
Initial-Consideration Set: Identification of need and initial research for brand consideration is the first stage for recognising actual needs in the hospitality industry (Liu et al., 2017). Feeling the need for hospitality service, such as a need for a vacation in the countryside, customers look for offers of hotels. Searching for information depends on the customer’s experience with the product and visibility on the internet. Visibility on the internet, Word of Mouth, and recommendations by peer groups play a great role in selecting a specific brand.
Active Evaluation: Customers find a range of brands providing the desired services. Alternative evaluation represents a specific state in which a consumer seeks alternatives that can provide the same quality services for fulfilling their own needs (Jahauri, 2017). After the customers receive information, they evaluate the alternative services offered in the hotel and finally select a brand for final purchase.
Moment of Purchase: The third stage is about purchasing decision-making in which a consumer can select Premier Inn as a desirable lodger which can provide desirable services within the budget range. The customer decision can be affected by advertising, recommendation of the hotel, their website, social media etc.
Post-purchase Experience: In the end, the fifth or last stage comes that aligns with post-purchasing evaluation, in which consumers can evaluate services provided by Premier Inn authority. For evaluating customer experience effectively and to deliver better services based on the experience-sharing process of consumers, Premier Inn always asks for feedback for its potential users.
Mapping a path to the purchasing decision in the hospitality industry:
The part of purchasing decision refers to the complete scenarios a customer passes while completing the transaction, from feeling the need to post-purchase behaviour. Mapping a part to the purchasing decision plays important role in the hospitality industry mainly because it provides the evaluated way of how a customer makes a purchase decision (Horner & Swarbrooke, 2016). Below, diagram shows that there are four stages in the map to path consumer decision-making.
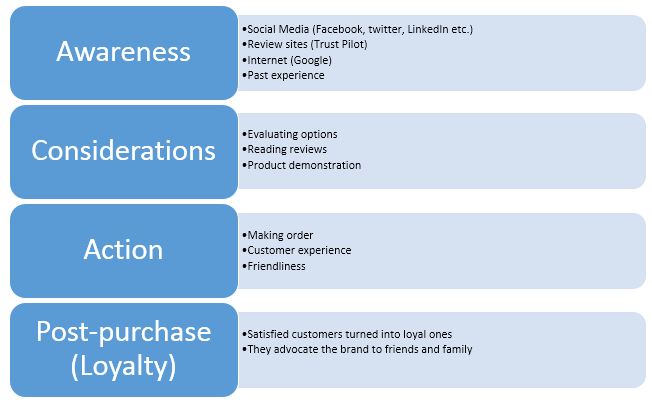
Awareness: At the first stage, customers grow awareness through browsing a number of communication mediums such as social media (such as Facebook, twitter, LinkedIn etc.), review sites (such as Trust Pilot), internet searches, and past experience in the same company (if any). In the case of the hospitality industry, such as Premier Inn., review sites, social media reviews, and active participation in social media play the most important role because customers highly value the opinions of the people who have already experienced the services (Parsons, Maclaran, & Chatzidakis, 2017). The reason is that the hospitality industry is highly dominated by personal reviews, which motivate new customers to make their decision.
Consideration: After being aware of the information and preferred services, a consumer does an active evaluation of the information and data (Zsarnoczky, 2018). Among the options, customer reviews which offers are more suitable than others and which hospitality company provides an excellent customer service experience than others. Reviews in the sites such as Trip Advisor, Yelp, and Trust Pilot are critically evaluated by customers who experienced services at certain hospitality organizations in the past. The customers carefully read the reviews, and these significantly affect the decision-making of the customers.
Action: This is about getting the real experience which starts with booking certain services at Premier Inn. A hospitality company should critically analyse how customers prefer to place orders and why certain order-placing methods are not adopted; it is important to understand the bottleneck of the certain process to streamline the service delivery process (Sudha & Sheena, 2017). Customers come into direct contact with the services and employees of the hospitality industry, and they develop a certain level of customer experience. A hospitality company must review the customer experience map to identify the touch points and the reasons for customer dissatisfaction.
Loyalty: The level of customer loyalty is demonstrated through the post-purchase behaviour of the customers (Liu et al., 2017). Customers who experience positive customer-experience are more likely to be loyal customers. Premier Inn must review the number of repeat customers and new customers. It is also important to understand why customers are dissatisfied to help the company solve the complications.
Importance for marketers to map a path to purchase and consumer decision-making in the hospitality sector
Understanding the consumer’s decision-making process and path to purchase plays a significant role for every marketer; it is even more important for hospitality companies. The reasons are analysed below:
Firstly, the Mapping path to purchase and consumer decision-making process allows a marketer at Premier Inn to know the touch points where customers contact the company in making decisions. This knowledge helps Premier Inn to optimize the Excellency of those touch points to motivate the customers to make a positive purchase decision.
Secondly, Mapping the path to purchase and consumer purchase decision allows Premier Inn to understand the pitfalls of the operations. It helps the company to optimize the drawbacks and attract more customers to obtain services for the hotel group.
Thirdly, it allows Premier Inn to identify the most important review sites and dominate social media forms where customers collect information while making the purchase decision. Consequently, the company can concentrate on developing the reviews and ranking in the dominating review sites. This affect consumer purchase decision positively.
Liu & Mattila (2017) stated that anticipated actions or barriers faced by decision-making processes, a mapping perspective allows responsible departments to ensure and project the best out of components considered by a consumer while making a purchasing decision. Above all, consideration of the opinion of Richard & Masud (2016) shows mapping process is also the easiest way to identify barriers that are hindering consumers from taking decisions in favour of a business entity.
Differences between B2B and B2C in the hospitality decision-making process
B2B stands for business to business in which the products and services are sold directly to the business entities and are used by them as final goods or as an intermediary (Bowie and Buttle, 2011). For example, Premier Inn’s business relationship with a corporate customer seeking regular accommodation support on a large scale is considered a B2B relationship. B2C stands for business to customer, in which the products are sold directly to customise and aims to build better relations with them (Bowie and Buttle, 2011). It is regular relations of Premier Inn with their individual customers.
The most prominent similarity in the consumer decision-making process between B2B and B2C is that both aim to meet a need through making the purchase decision. Both follow the same decision-making process. However, how they follow the stages and their relative perceived importance in each stage are different.
B2B relationship is small-scale oriented and this is for a niche market where niche focus (as per Porter’s Generic Strategies) gets priority (East et al., 2016). As a result, customers in B2B look for cost reduction and such customers would conduct a wide range of possible options from other companies. For example, the previously mentioned corporate client would look for cheap room rent from Premier Inn because they would rent rooms on regular basis without adding much value. In contrast, B2C is dominated by a large-scale market because there are a large number of customers seeking hospitality services (Alavi et al., 2016). Consequently, such a market is dominated by differentiation and added values where customers are ready to pay premium prices. For example, individual customers would expect added values such as state-of-the-art technologies from Premier Inn. Since the impact of decisions in B2C is less impactful than in B2B, customers are B2C conduct fewer searches than those done in B2B.
Another potential difference is that customers at B2B directly contact the hospitality company because such customers have high bargaining power. In contrast, customers at B2C have relatively less bargaining power over the hospitality company because individual customers are less important than the bid-sized customer. As a result, a B2B customer directly deals and negotiates with a Hospitality Company; and individual customers in B2C take help from social media, and review sites to assess the credibility and service quality. To illustrate, the corporate client would directly negotiate and contact Premier Inn to settle the prices because it has high negotiation power. On the other hand, customers in B2C need to check Trust Pilot, Trip Advisor, and social media reviews to make decisions.
Different approaches to market research and methods of research to understand the decision-making process
Understanding the decision-making process in the hospitality industry would require either primary or secondary research. In both cases, the research approach and research methods are important elements.
Approaches to market research: Inductive and Deductive
Research approach refers to the research styles which will be followed to conduct the research (Guercini, 2014). Marketing researchers generally follow two types of research approaches: inductive approach and deductive approach. If the research hypothesis is not outlined at the beginning of the marketing research, an inductive research approach is used and it aims at conducting in-depth research to generate theories (Krafft et al., 2015). The advantage of this approach is that it conducts in-depth analysis and evaluation. However, a drawback is that this approach is little probability of yielding a research outcome. On the other hand, the deductive research approach is used when the research hypothesis and theories are outlined, and the research aims to check if the theory is right (Guercini, 2014).
The selection of a research approach depends on the type of research. For example, if research on the consumer decision-making process follows the qualitative research method, the approach would be inductive because the qualitative method conducts in-depth analysis and evaluation. On the other hand, it would follow a deductive research approach is the method were quantitative.
Methods of market research: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Hybrid
Research methods refer to the way through which research will be conducted. The figure shows different research methods available to use for research in the hospitality industry domain.
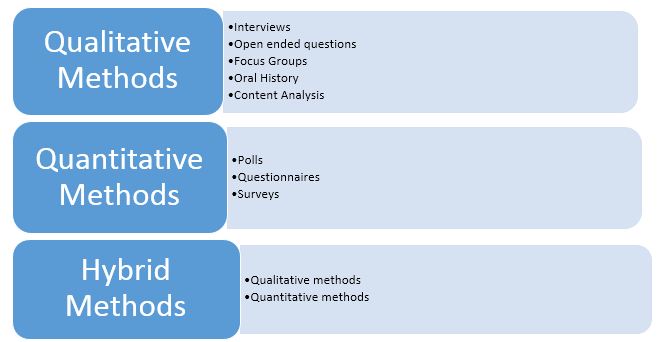
Qualitative methods have different options, such as interviews, open-ended questions, focus groups, oral history, content analysis etc. (Baron, Warnaby, & Hunter‐Jones, 2014). The advantage of these methods is that it is broad and conducts extensive analysis. However, the problem is that it cannot yield a quantitative result. The selection of a certain method depends on the research topic and research objectives. Quantitative methods also offer a range of options, such as polls, questionnaires, and surveys. The advantage of the quantitative method is that it comes with quantifiable outcomes. The drawback is that it cannot include detailed feedback from the respondents (Malhotra, Birks, & Wills, 2013). However, hybrid methods use both quantitative and qualitative methods, and it overcomes all the barriers experienced by each method individually.
For research in the hospitality domain, the selection of the research method is completely dependent on the research objectives and expected outcomes.
How marketers influence different stages of the hospitality decision-making
In the hospitality industry, marketers can play a significant role in every stage of the consumer decision-making process. The influence can start with the initial-consideration stage when consumers feel a need and check the available options to meet their needs (Szmigin & Piacentini, 2018). For example, markets at Premier Inn could make the advertisement and exposure in a such an excellent manner that customers feel the need to experience the service even if this is not mandatory for them. Thus, it can be seen that markets can motivate customers to avail a new need even if that is not mandatory.
Secondly, marketers can play a role in making them the most visible and attractive company among all available options (Gavilan, Avello, & Martinez-Navarro, 2018). For example, marketers at Premier Inn can do SEO to represent themselves at the top of search engine results, can do Google advertisements to increase visibility, and can be highly active on social media in attractive ways. All of these options can play an important role in motivating customers to act in a certain way in making decision.
Thirdly, marketers can increase their rating on the review sites by motivating and providing lucrative offers to past customers to post their good experiences at the review sites on the internet (Hu & Yang, 2019). For example, Premier Inn can motivate its previous customers to put positive reviews on Trust Pilot, Yelp, or in Trip Advisor or in Facebook with an offer of 10% discounts for all reviewers. This would significantly change the company’s outlook on social media and motivate customers to make a consumption decision in favour of the brand.
Finally, marketers can continue regular communication with the customers to keep them informed and motivated. As a result, past customers will be repeated customers, and customer loyalty will be high.
Conclusion
Aspiration to produce an understandable account regarding consumer behaviour and decision-making process as well as purchasing intention drove this study towards the analysis of several factors and components associated with the hospitality industry. In this perspective, the evaluation of the contemporary practices of Premier Inn has entrenched consideration of consumer buying behaviour analysis as an essential part of business outcome evaluation. Terrestrial digital transformation is bringing several changes in the consumer behaviour process, and this has been illustrated by involving a process map for the decision-making process. However, on completion of the evaluation, consumer behaviour can be considered the most prominent controlling factor of business in the hospitality industry.
References
Alavi, S. A., Rezaei, S., Valaei, N., & Wan Ismail, W. K. (2016). Examining shopping mall consumer decision-making styles, satisfaction and purchase intention. The International Review of Retail, Distribution and Consumer Research, 26(3), 272-303.Bowie, D., Buttle, F., Brookes, M., & Mariussen, A. (2016). Hospitality marketing. Taylor & Francis
McKinsey & Company, (2019). The consumer decision journey. [Online] Available at: https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/marketing-and-sales/our-insights/the-consumer-decision-journey [Assessed date 01 August 2020]
Premier Inn., 2020. About Us. [Online] Available at: https://www.premierinn.com/gb/en/why.html [Assessed date 31 July 2020]
The Telegraph (2014). Premier Inn goes high-tech [Online] Available at: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/travel/news/Premier-Inn-goes-high-tech/ [Assessed date 31 July 2020]
Zsarnoczky, M. (2018). The digital future of the tourism & hospitality industry. Boston Hospitality Review, 6.
