Introduction
International Marketing Performance of Uber will be analysed in this blog. Global marketing is the extension of marketing activities in the global scale in which a company utilizes the international opportunities as well as national opportunities through creating and adding value with existing products and services. This report has critically analysed and evaluated different international marketing models, methods, and strategies to see their reflections in the international marketing performance of a company. The selected company is Uber.
You may also read the post:
External Environment Analysis of KFC
Background to selected company: Uber
Globally, Uber is the largest transportation company who doesn’t own any vehicle. It is a US based ride-sharing Corporation which was established in 2009 and which has operations in 63 countries in more than 780 metropolitan areas (Uber Technologies Inc., 2020). This is a peer to peer ride sharing service in which a registered vehicle owner can provide a ride service to an Uber customer in any Uber service area. The company has more than 22,263 employees in its 63 operational countries where the number of users of their mobile based app is 110 million (Statista, 2020). Uber adopts different strategic options to expand the business in new countries, for example it went to Russia through a joint venture with a Russian rival called Yandex and went for FDI in India; on the other hand Uber couldn’t sustain the competition with a Chinese company called Didi; as a consequence the company had to leave China.
International Marketing Performance of Uber
Internationalization Motives influencing Uber to move into new International Markets
Unique business idea, untouched potentials in global market both in demand and supply side, excellent marketing opportunities are the most potential reasons that motivated Uber to go International in 63 countries.
Optimization of use of innovation advantage in global scale: The business idea and the platform to connect a free driver with a passenger were unique identification of untapped potentials persisted in global market. Uber carefully understood the potentials and opportunities of expanding the ideas across countries. It did the expansion globally and the result of such expansion is impressive making Uber world’s largest transportation company without owning any vehicle of its own.
Untouched supply potentials: Uber doesn’t have any supplies which mean it doesn’t conduct any production, rather individual vehicle owners are supplies themselves. Uber identified that there are hundreds of thousands of such supplies, moving across major cities of the world, who can accompany other people who have the same destination. Business of Apps (2020) has revealed that there are 3.9 million Uber drivers globally. Thus, it has correctly assumed the market potentials.
Huge demand in global market: The Company assumed that a connection should be made between city travellers and people moving with vehicles. Identification of the potentials was correct, as a result Uber expanded the business globally in less than 10 years. Business of Apps (2020) has found that Uber completes on an average 14 million trips every day and it completed well above 10 billion trips till date. Surely, Uber’s assumption about untapped demand side was correct and it highly motivated Uber to expand.
Economics of scale: Opportunities for completing more jobs at less resources attract all businesses to expand internationally, it also motivated Uber. Uber already had a website and mobile based app platform through which users could communicate. Expansion of the facilities to more markets would enable the company to experience economies of scale. The result is impressive because Uber made a revenue of $11.3 billion in 2018 which is an increase of 43% from previous years (Business of Apps, 2020).
Diversification of risks and sourcing new talents: Doing business in one market is more risky than doing business in multiple markets because risks are distributed in multiple markets. This factor motivated Uber to expand the business in international market. Now the company can optimize risks through distributing the business and risks globally.
Analysing International Marketing Performance of Uber by Applying Global Marketing Models
International market selection process
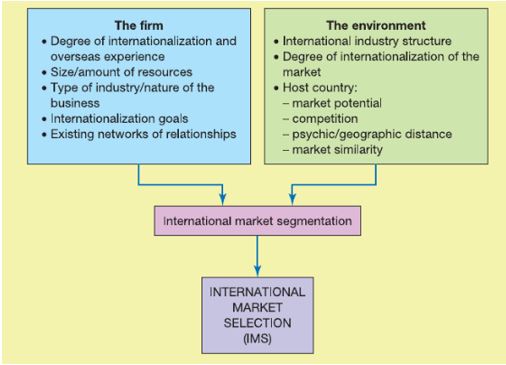
Above figure 1 demonstrates a company go through international market selection through a process and a number of factors such as international experience, size, type of industry, market structure, host market scenarios etc. affect selection decision.
Ansoff Growth Matrix Application on Uber
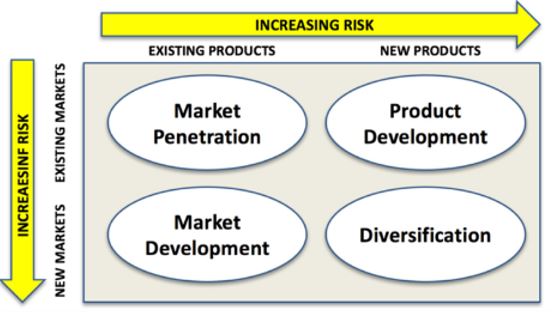
Above figure 2 shows there are four strategies of business expansion: diversification, market development, product development and market penetration among which diversification poses the highest risks with potential chances of returns.
Comparison of two market potentials (Uber Canada and Uber India):
Two international market of Uber have been selected: Uber Canada and Uber India. A comparative statement with evaluation of choice has been presented below with application of two models shared above.
| Uber Canada | Uber India |
| Canada has a population a little above 38 million in 2019, GDP of $1.97 trillion in 2019 and GDP per capita is $52,144. | India has a population about 1,352 million in 2019, GDP of $12.363 trillion in 2019 and GDP per capita is $9,027. |
| Ride-sharing industry in Canada is amount to $1,700m market (a decrease of 36% from previous year) with a number of users of 8.2m. | Ride-sharing industry in India is amount to $26,153 m market (decreased by 33% from previous year) with a number of users of 295.9 m. |
| Female to male customer penetration rate is: 50% : 50%. | Female to male customer penetration ratio is: 32:62 |
| In Canada, a large number of customers aged in between 45 to 64 years take Uber Services. | In India, a large number of young customers aged in between 18 to 35 take the services. |
| Given relatively small number of population, the number of trips in Uber’s Canada operation is much less than those in India. | Uber India has over 5 million active riders in India in a week which is 40% of the total market share in the country, Ola is the main competitor with market share of 56%. Ola is a domestic company in India. |
| When Uber started its ride-hailing services in Canada, it was market development approach because product was established and market was new. | Ride-hailing services in India was also market development approach. |
| Uber Eat was a product development approach because market was known but product was new. | Uber Eat was a product development approach in India because market was known but product was new. |
Clearly, Indian market is much more attractive, sustainable and lucrative then that of Canada because the huge number of population in the country and a stable economic and political condition. Penetration rate of male to female in Canadian market is better than that in India. Uber faces severe competition from Ola in Indian market. However, Uber Eats have huge potentials in India and the company should do aggressive marketing in India to capture more food market share.
Market entry method and evaluation
Market entry modes refer to the way through which a company enters a foreign market in order to expand the business. There are different entry modes such as licensing, franchising, joint venture, FDI, exporting, online sales etc. which has specific advantages and disadvantages of their own. A company should select the entry mode based on the nature of business, competition, required level of controls on the business etc. In this analysis an international market of Uber has been chosen: India.
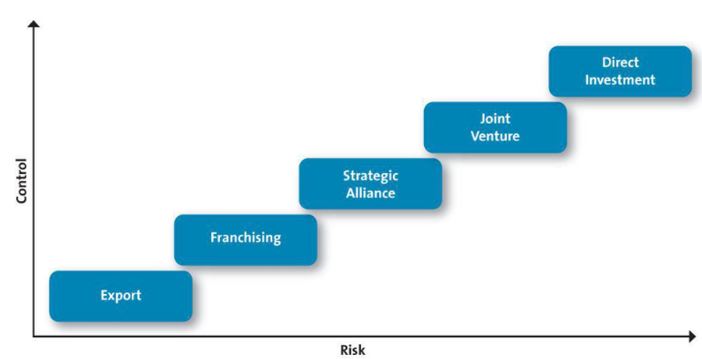
Your Story (2013) has revealed that Uber started its operation in a small scale in a city of India: Bangalore with a few employees. This implies that it made Greenfield investment which is alternatively called Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). The company surely took right decision about the entry strategy to Indian ride-hailing industry because it offered Uber complete control on the whole operation, to maintain high-class quality, to keep the strategies and confidential data secret, to keep the app in control and so many other reasons. In below section, the justification in details of how FDI was a better decision for Uber to enter India is evaluated below.
The strongest proponent for FDI of Uber in India is that it enabled Uber to have stringent control on the expansion strategies, on qualities, and operational services. Without direct investment, Uber wouldn’t have such strict control on the operations.
Secondly, the future potentials of Indian ride-hailing and food logistics industry in India clearly offers an attractive future for a company like Uber. The company needed to keep having experience on the demographic features of the customers, their preferences, economic conditions and macroeconomic scenarios. Without FDI, such experience wouldn’t be possible.
Thirdly, FDI of Uber in India has enabled the company to avail preferential tariff and taxes advantages which wouldn’t have been realized had the company not adopted FDI. As a result, Uber now realizes tax and tariff benefits.
Finally, India is geographically an important region in the South-East Asia and it has considerable dominance in the region, thus having presence in India has enabled Uber to gain invaluable experience of competition. Moreover, it has equipped the company with much need market data, trends and experience needed to operate Uber in other countries in the area.
Marketing strategies Uber used in India
Marketing strategies refer to the approaches companies use to reach customers. In this section, marketing strategies of Uber in India has been evaluated.
Discounts and cash-back played great role: This refers to a financial system in which service users will get discounts or money-back deals after using a specific service. Uber played this tricks widely to expense conscious Indian consumers and it worked so nicely that contemporary followers also followed the same strategy. This strategy positively motivated Indian customers and helped them to avail the service. However, this strategy is not a sustainable approach because a company cannot follow this strategy in long-run because of substantial financial losses.
Referral options: This is a system in which a user can suggest others about the services, if the referrals use the services, referee gets bonus or referral incentives. This also play potential role among the perception of a large number of customers because this takes little effort. Uber used this marketing strategy both in vehicle-hailing services and in food-transport services. The increasing number of customers of the company and a growing market share imply that the strategy worked nicely in the Indian market.
Review system: Uber app has options in which the service users can rate the service providers at a scale of 5. This allows a new service users to find the level of service with rating. This is an excellent approach of Uber because it helps the customers to know if the level of service is poor. On the other hand, it also allows the service providers to see the professionalism and manner of the customers through the rating since service providers are also capable to rate their customers. Such rating system creates excellent opportunity for both parties to ensure well-mannered behaviour.
Partnership: Another marketing strategy of Uber is that it does contact with a large number of partners such as hotels, resorts, airlines, restaurants. For example, Uber declares that customers leaving from this hotel to certain area will get a discount of some percentage in Uber trips. This is a win-win situation for all the participating parties: Uber, customers and the partners.
Conclusion:
A company goes international for untapped potentials in international market. Uber detected huge untapped potentials both in the supply side and in the demand side, moreover the company has successfully expanded the activities in more than 60 countries. Presence of Uber in India and in South-East Asia is of great importance for the company for huge population and economic expansion.
References
Business of Apps (2020). Uber Revenue and Usage Statistics (2020). Retrieved from: https://www.businessofapps.com/data/uber-statistics/ [Assessed on 5-May 2020]
Statista, 2020. Monthly users of Uber’s ride-sharing app worldwide 2016-2019. Retrieved from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/833743/us-users-ride-sharing-services/ [Assessed on 6-May 2020]
Uber Technologies Inc., 2020. Use Uber in cities around the world. Retrieved from: https://www.uber.com/global/en/cities/ [Assessed on 5-May]
