Introduction:
Strategic Human Resource Management Models will be evaluated in this report. Strategic management of the HR resources refers to the management of employee attraction, recruiting and retention through training and development as per the business objectives. This report has critically viewed into the relationship between business strategies and HR strategies with extended view on horizontal and vertical integration. It has also included different views such as best fit, resource based view. The report has also critically reviewed the HR practices of performance management.
You may also read the blogs:
Importance of Checking Candidates’ Social Media Profiles
Link between Business Strategies and Human Resource Strategies
Before analyzing the linkage between business strategies and HR strategies, it is important to define the terms.
Every business has some goals and objectives to achieve, and businesses also has a set of approaches and routs to achieve those goals. Above goals and routs are considered as business strategies (Daley, 2012). Business strategies play significant role in every organizations and without the strategies a company cannot sustain in the long run. Moreover, businesses will lost in the competition without solid business strategies.
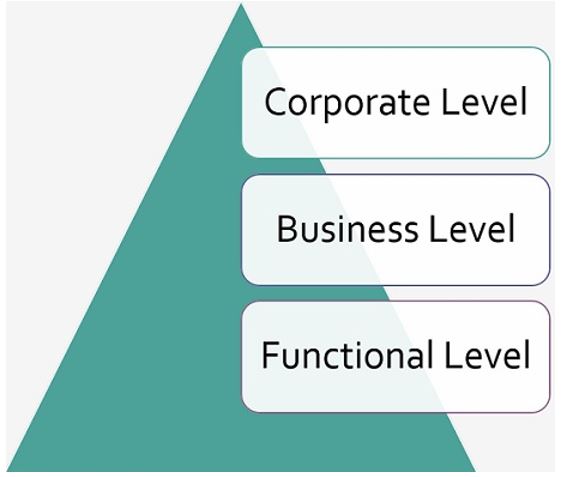
Above diagram shows that a company can have three levels of business strategies: corporate levels, business level and functional level (Mello, 2014). Corporate level business strategies play the most important role because it determines what the business should achieve and how everyone should work to achieve the corporate vision and long term goals.
On the other hand, HR strategies are a comprehensive plan of setting the HR policies, determining the qualities and capabilities of employees, attracting talents, recruiting the employees, training the developing the employees to ensure that they can reach the business objectives and finally taking actions to retain the talents (Wright and McMahan, 2011).
Above definitions of business strategies and HR strategies reveal that they have very close relationship. In fact, business strategies cannot be implement if HR strategies do not coordinate to achieve business strategies (Lengnick-Hall, Beck and Lengnick-Hall, 2011). Similarly, HR strategies are meant to help the company to achieve the corporate level strategies, business level strategies and functional strategies. For example, British Airlines have a plan to be the best chosen airlines with same level of state-of-the art services at all operational locations. This is a corporate strategy. HR department of the company must make their HR strategies. To further exemplify, the HR of British Airways should recruit the best talent and train them in such manner that they become capable to achieve the corporate level strategy. Above example shows the integral relationship between HR and business strategies.
Strategic Human Resource Management Models
Vertical alignment:
The term vertical alignment refers to a corporate level business strategy which implies that a company wants to have control on all the value chain over the industry (Boselie, 2010). To exemplify the situation, Unilever produces the raw materials, use the raw materials to make soap, do marketing communication and after sales services. This is an example of vertical alignment where Unilever has control on all the value chain stages of the supply chain.
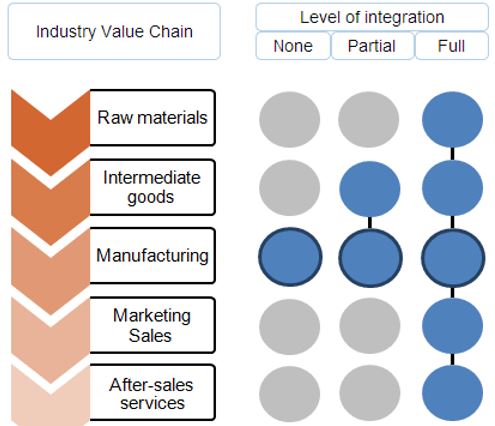
Vertically aligned company has full control on complete value chain stages of the industry supply chain (Jackson, Schuler and Jiang, 2014)
If a company will be vertically integrated or not depends on the corporate level strategy of certain company. Corporate level strategies consider two factors while deciding if a company should be vertically aligned: costs and scope of the firm (Jackson, Schuler and Jiang, 2014). If the costs of producing raw materials (in case of Unilever from above example) is less through being vertically aligned than procuring the materials from outside, the company should follow vertical integration. Additionally, the company should also consider the competitiveness impact for being vertically aligned. HR strategies are directly linked with above decision, in fact, HR should make their recruitment and training plan based on the selection of strategies.
Horizontal integration:
Horizontal integration refers to either acquiring a similar company or merge with a competitor to enhance the economies of scale, to enter new market, to strengthen the competitive position, to reduce the competition (Huselid and Becker, 2011). This is a corporate level strategy which aims to merge or acquire another company in the same industry.

Horizontal Integration merges or acquire another company in the same industry. To exemplify the situation, Lafarge is a global cement brand, this company merged with Holcim, another global cement brand. This is an example of horizontal integration in which two companies merge with each other for many reasons.
HR strategies are closely related with above strategies. Mergers or acquisition involves replacement of employees in two organizations and such management of employees requires careful handling and management.
Strategic Human Resource Management Models: Best practice view of HRM
Best practice view of HRM reveals that there are a set of universally accepted and researched HR practices that result in superior business performance regardless of the types of industry (Kramar, 2014). Best practice view proposes that a company should have the set of best practices HR strategies in place to ensure that the company achieves the business objectives. Some of such best practices include to provide security and safety to employees, to hire the right people, to ensure self-managed teams, to ensure fair performance appraisal system, to ensure training and relevant skill development to name a few.
Strategic Human Resource Management Models: Resource Based view model
Resource based view of HRM argues that the sustainability and competitive advantage of a company depends on the strength of the resources it has (Armstrong, 2011). Companies following resource based view emphasize on competitive advantage inside the business instead of looking to the competitive environment of the business.
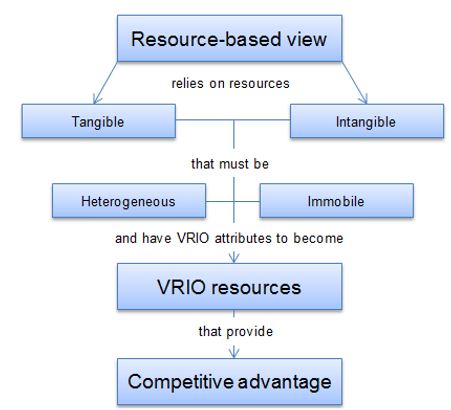
Companies emphasizing on resource based view observe in resources based on Value, rareness, inimitability and organization (Armstrong, 2011).
Above diagram implies that resource based view critically evaluates the internal strength of a company and the resources based on their Value, rareness, inimitability and organization. It argues that it is important to increase the value of competitive advantage of the resources and capabilities.
Strategic Human Resource Management Models: Best-Fit model
Best-Fit model argues that a company should select the suitable strategies of HRM based on the internal business environment, external business contexts (Gratton, Hailey and Stiles, 2011). The model also proposes that there is no universally accepted set of models or strategies, rather the strategies and practices should be determined based on the business context, business environment and competitiveness. Truly, best-fit model makes excellent sense because the strategies should of course be selected based on the context of the business because a set of strategies suitable for one company might not be appropriate for other companies.
Comparison among Resource Based View, Best Practice and Best-fit Model:
Among four views analyzed above, resource based view is surely applicable because of the value of the model which emphasizes on strengthening the values and capabilities of the company. This model will be helpful for all companies regardless of sizes or locations. There is a competition between best practice model and best-fit model. Best practice model suggests a set of practices which couldn’t be suitable for companies or sizes. On the other hand, best-fit model suggest only those practices and strategies which are suitable based on the internal and external business and competitive scenario. From above, it is clear that best-fit model is much more strategic and suitable for a company.
Critical evaluation of HR practices of performance management and rewards:
Employees can be motivated, engaged, and empowered in a number of approaches. In this section, the HR practices and performance management and reward approaches have been analyzed.
Best performer award: This means a company can sincerely evaluate the performance of the employees and award the capable employees with best performer. This will significantly enhance employee performance; as a result they will be engaged, motivated and retained.
Respect and admiration: This means a company should uphold respect and admiration to the employees and their valuable work. As a result of this, employees will feel respected and honored which will significantly boost the psychological acceptance for the company.
Celebration: This means a company should celebrate small winning and results through small celebration whenever possible. This will make important sense of doing great jobs in the workplace because small celebration events will encourage the employees to undertake similar efforts in future.
Fair assessment and evaluation: This is an excellent strategy to employee evaluation and performance management. It will help the employees to think positively because of the fair assessment.
Above analysis shows that a company should undertake HR performance evaluation and reward techniques very carefully to ensure that employees are motivated, empowered and engaged to exert the best performance to achieve business objectives.
Recommendations on how to make better design of performance management system:
Performance management system in organizations should not be generic because corporate objectives, nature of business etc. are not same across the organizations (Marler and Fisher, 2013). Therefore, performance management system should be tailored as per the business objectives and capabilities.
Firstly, HR of a company should know the corporate visions and objectives, business objectives and strategic priorities because knowing these will make the background of deciding what to implement (CHUANG and Liao, 2010). Based on objectives, HR should determine the strategies and objectives of the HR department.
Secondly, based on the objectives and newly developed strategies, HR then should determine what resources they need in HR (Lengnick-Hall, Lengnick-Hall and Rigsbee, 2013). It should also examine the capabilities, expertise, and experience needed among the employees. Most importantly, they should understand the skills, capabilities and expertise needed by the managers and leaders.
Thirdly, HR should determine needs for training and development for employees. Step mentioned in second stage will help the company to determine what training and development employees need. HR should make detailed plan of training schedule, contents.
Fourthly, HR should set performance targets, desirable goals, and team performance parameters. This will help employees to act according to the set goals and objectives.
Finally, HR should make a critical review on the rewarding system, level of employee engagement and motivation, employee retention to make a comprehensive plan to revive all the parameters (Sani, 2012). Such plan should aim to make HR reward system fair and acceptable, to make employees more engaged and motivated ensuring that retention rate is high.
Nature of employee relations
This segment has critically analyzed the theoretical perspectives of employment relations and the roles played by major actors in employment relations. The nature of employment has changed over the time. In this changed scenario, how employees’ voice can play role in employment relation has also been discussed. In both segments, some recommendations have been given.
Nature and theoretical perspectives of Employee Relations:
Nature of Employee relation:
Employee relation refers to positive relation between employees and a company, wise companies put high efforts to keep congenial and reliable employee relation (Paille et al., 2014). There is linear relationship between employee relation and performance of the company. This implies when employee relation is highly positive, company performance is like to be highly positive as well and vice versa. Friendly and positive employee relation results in good performance because these employees are highly motivated, engaged and inspired to achieve the objectives of the company (Snell, Bohlander and Bohlander, 2010). Some companies maintain employee relations management department to ensure that a profitable relationship is maintained with the employees.
Employee relations implies individual relations and collective relations where individual relations refers to relation between individual employees and employers; this also implies relation between trade unions and the management committee (Jiang et al., 2012).
Jiang et al. (2012) have also revealed that employee relations can be of different dimension including trade unions, government, regulatory authority, trade association and the company itself. A company has to carefully observe the nature of different dimension and then should carefully determine the nature of relation with the trade unions.
Finally, employee relations is a dynamic concept which has been changing and will be changing due to the nature of the subject (Buller and McEvoy, 2012). The reason of such changing nature is that new laws, new issues are being added with the subject and thus the nature of relations has also been changing.
Theories/models of employee relation (ER):
Models of Employee Relation (ER) critically view into the nature of relationship between employees and employers. Understanding ER model is important to know the factors that affect employee relations and to create excellent relation between employees and employers along with a contribution of government regulatory bodies.
Unitary Model of ER:
Organizations following Unitary Model believes that all the employees consist a team and there is no division (Noe et al., 2015). Such philosophy brings outstanding result because employees and workers believe that they are part of the team and their necessities are taken care of by the company. An ideal company should uphold the spirit of one team approach to make positive impact through employee engagement, high motivation and high talent retention.
Critical model of ER
Critical model of ER implies that there is difference between decision maker and the implementer, such philosophy is led by the concept of differences in power and economic perspectives (Besma, 2014). This model indicates that investors and top management of a company have the complete authority to make decision whilst workers should implement the directions even if the directions are capitalistic and pay little hid to the interest of the employees. As a result of such philosophy, tension grows among employees and employee relation becomes worse.
Pluralism model of ER:
Pluralism model of ER suggests that relationship between a company and employees should be democratic in which a mediator should play role to make negotiation and agreement between trade unions and the company itself (Stahl, Bjorkman and Morris, 2012). This is a democratic approach to employee relation in which interest of both trade union and those of the company is protected, as a result both parties are satisfied.
How the actors play a role in employee relation:
An organization has different bodies from internal and external environment and they play important role in employee relations. Extent of success of employee relation and failure in employee relation take place due to the differential impact from the actors. Their roles are analyzed below:
Leaders and managers play the key roles in making decision regarding employee relations and to erect bridge in between top management and employees of a company (Jiang et al., 2012). In one side, company’s norms, corporate objectives are rightly known by leaders and managers who actually take active part to make them; in another side, leaders and managers convey the message and make communication with rest of the employees whose fathom affect employee relation. This is clearly shown that leaders and managers play significant role in employee relation.
Employees and workers are the groups who originally matter the most because growth of a company depends on how they perceive a company and its vision towards them (Martocchio, 2011). If employees have strong fathom that top management and stockholders view them as part of one team, employees and workers will be highly motivated, engaged and retained to achieve the company’s vision and mission.
Trade unions are groups formed by workers to take care of workers’ well-being, unity etc. (Sparrow, Brewster, and Chung, 2016). Trade unions are formed in factory based organizations which have workers. They play important role to make bridge between workers and top management of a company. Leaders of trade unions negotiate with top management to bargain for the best results of general workers.
Investors are stockholders of a company and their preferences, decision are reflected in the manner of how a company make relations with its workers and employees (Hendry, 2012). Investors generally work for their interest, however, they should be logical in their decision.
Government regulatory bodies play significant role in employee relations because their decision affect both the company and employees (Adegoroye, Oladejo, and Moruf, 2012). Government regulatory bodies should be neutral in their decision to protect interest of both company and employees.
Changing nature of employee relation:
The nature of employee relation has been ever changing due to changing nature of employment laws, relation between employees and owners and most importantly because of globalization.
Firstly, nature of bargaining between workers, employees and owners has changed. In the past, the relationship between them was biased and owners would exploit the workers in many cases which has changed a lot in recent decades mainly because of globalization and more civilized approach to employment (Storey, 2014). Now, owners count the preferences and bargaining power of the employees and workers.
Secondly, there has been a democratic approach in decision making across the organizations in which employees and workers have strong say on decisions made by a company (Wright, Coff and Moliterno, 2014). Such has happened based on consideration that employees’ engagement in decision making results in motivation and high employee retention because of the participation.
Thirdly, safety of the workers, workplace hygiene, and job security plays significant roles in employment relations. Such initiatives have highly motivated to be engaged in the workplace. This has also positively affected employee relations.
Recommendations on how employee participation and voice can help to improve employee relation:
A number of steps and strategies can be followed to encourage employees and workers to raise their voices. Companies should pay close attention to the voices of employees.
Companies should encourage workers to form trade unions because trade unions are organized way through which workers can express their opinions (Budhwar and Debrah, 2013). Such opportunities will empower workers in an excellent way to express their views. As a result, employee relations will improve.
Participative voice and assessment involvement will play important role to improve employee performance (Jackson et al., 2011). Employees should be encouraged to assess their performance first, then HR should assess performance of specific employees. As a result, participated employees will come to know the evaluation from two perspectives and reflect further on their activities.
Employees should be encouraged to take part in meeting and to make a contribution in decision making. As a result, they will be involved with the decision making process and they will be encouraged to implement the decision.
Employees should also be involved with salary evaluation. This will help the company to understand expectations from employees and will help them to reflect on salary decision.
Conclusion:
Business strategies and human strategies are closely related to each other. Human resource strategies and compiled based on business strategies. A company can follow vertical alignment or horizontal alignment, decision depends on the capability, competitiveness and nature of business. Among the models of SHRM, best fit model is most suitable considering its applicability and suitability in different scenarios. A company should also follow resource based view model because it will equip the company to emphasize on enhancing capabilities and competitiveness. Employees and workers should be engaged with decision making because it empowers employees.
Reference List
Armstrong, M., 2011. Armstrong’s handbook of strategic human resource management. Kogan Page Publishers.
Adegoroye, A.A., Oladejo, M. and Moruf, A., 2012. Strategic human resources management practices in the post consolidated Nigerian commercial banks. European Journal of Business and Management, 4(15), pp.168-176.
CHUANG, C.H. and Liao, H.U.I., 2010. Strategic human resource management in service context: Taking care of business by taking care of employees and customers. Personnel psychology, 63(1), pp.153-196.
Stahl, G.K., Bjorkman, I. and Morris, S. eds., 2012. Handbook of research in international human resource management. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Wright, P.M., Coff, R. and Moliterno, T.P., 2014. Strategic human capital: Crossing the great divide. Journal of Management, 40(2), pp.353-370.
